French archaeologist Stephen Rostain has revealed the existence of a city on the basis of evidence found in the Ecuadorian Amazon after two decades of research and field work.
Table of Contents
Structure of the ancient city
It is known that the city existed some 2500 years ago and proofs indicate that it was home to as many as 30,000 individuals. Radiocarbon dating stated that the area was inhabited from 500 BCE to between 300 and 600 C.E after which the site was left abandoned. No reason behind this has yet been known hence heavy growth of vegetation covered the region. This makes the city one of the oldest so far in the whole region of Amazon.
The director of the Investigation at The National Centre for Scientific Research in France revealed that it was discovered in the Upano Valley in the eastern foothills of the Andes where the Kilamano and Upano cultures once settled.
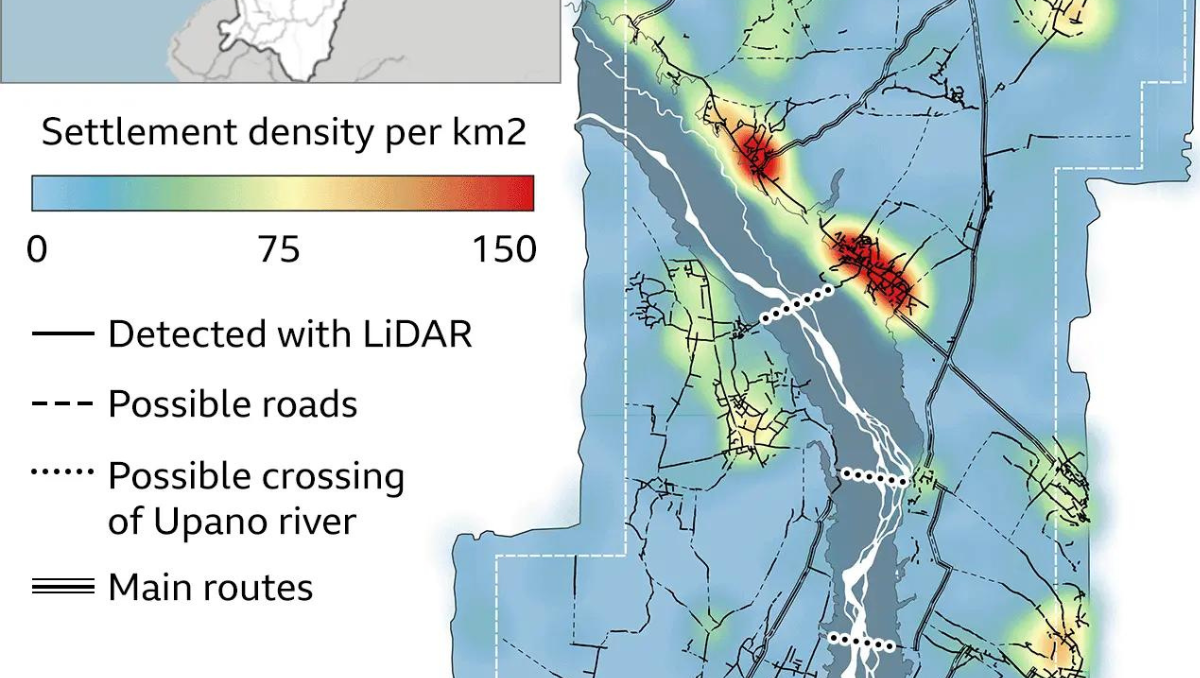
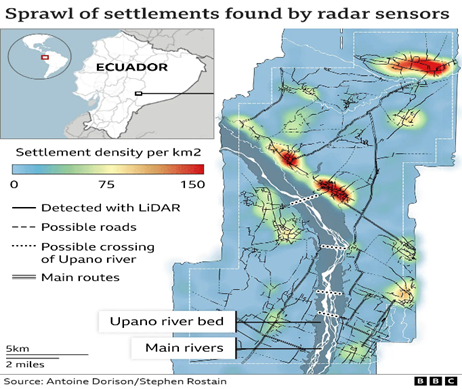
Spanning approximately, 115000 square miles, the urban complex was examined using a remote sensing, laser scanning technology Lidar Light Detection and Ranging). The size of the city can be compared to the current size of Egypt’s Giza Plateau.
Prehistoric Edifice
Lidar surveys showed that the site had plazas, roads, canals, homes etc. Archaeologists are of the view that these houses were built by cutting down hills into platforms of earth. Comprising over more than 6000 such earthen platforms arranged in a geometric layout, along with agricultural terraces and drainage systems, the region also contains huge mounds and monuments. In addition to this, wide straight roads extended throughout the town covering up to 30miles.
Antoine Dorison, an archaeologist at the National Centre for Scientific Research CNRS, said that the society’s complexity is especially evident in this web of streets, which were carefully constructed to cross at right angles rather than follow the landscape.

The area is situated beneath the shadow of a volcano which resulted in the formation of rich local soils. Inhabitants were mostly agriculturalists and the major crops cultivated by them were corn, sweet potatoes etc. Rostain theorizes that the decline of the sites may due to eruptions of the Sangay volcano.
Sangay is one of the most active volcanoes in South America active located in Ecuador. It is characterized by lava flows, pyroclastic flows and is also a part of the Pacific Ring Of Fire.
Amazon challenging our conceptions
Antoine Dorison further highlights the transformative impact of these findings on our perception of Amazonian cultures. People tend to create an image of naked groups of nomadic people usually food gatherers, roaming around in search of new shelters. But these findings give us an idea that the primitive people lived in complicated societies.
Evidence of a city was initially uncovered in the 1970’s. However, after 25 years of extensive survey and research work with further proofs and details the genuine presence of a city can now be established.
What is Lidar?
Lidar, an acronym for light detection and ranging uses laser light to measure distances between the earth and an object. It works in a way by sending laser light from a transmitter and then calculates the time taken for the light to reflect from an object.
Lidar systems consists of three parts Laser ranging system, Global Positioning System (GPS) and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU).

If there is one way to describe Amazon then it is through this line that: Time’s embrace hold secrets untold. In the heart of dense amazon rainforest filled with green canopy, there still lies a realm of mystery and intrigue. It feels as if with every excavation more and more hidden treasures are sprouting out revealing a new chapter of history. No doubt, that Amazon is a world of awe and endless possibility.